√70以上 stress at yield point formula 144974-How to calculate the yield point
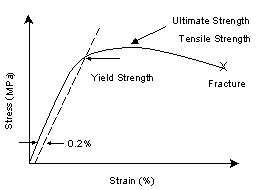
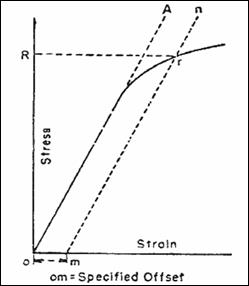
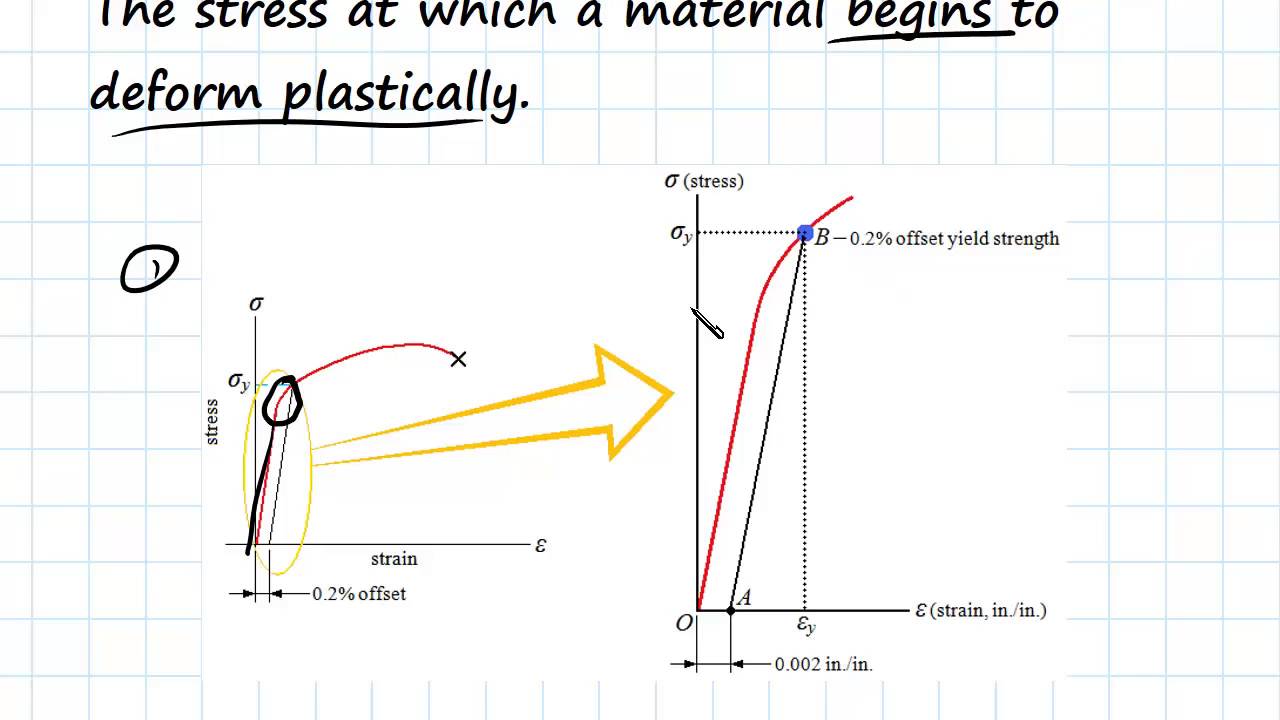
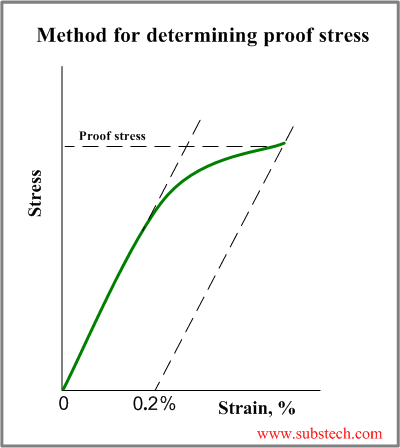
The yield strength at 02% offset is determined by finding the intersection of the stressstrain curve with a line parallel to the initial slope of the curve and which intercepts the abscissa at 02%The shear yield stress k can similarly be found by inserting the principal stresses corresponding to a state of pure shear in the Mises equation The point where the craze locus crosses theHowever, whereas u n is a scalar, S(n) in the equation (7) is a vector
Efatigue Glossary Ultimate Strength
How to calculate the yield point
How to calculate the yield point-YIELD STRESS MATHEMATIC APPLICATION F/A FORCE AREA = STRESS= FORMULA 1 A sample of steel ( from an engineering company) is given a stress test to assess its yield stress The steel is a mm square section The sample begins to yield at 30 000 Newtons What is the yield stress?Yield point, in mechanical engineering, load at which a solid material that is being stretched begins to flow, or change shape permanently, divided by its original crosssectional area;



Efatigue Glossary Ultimate Strength
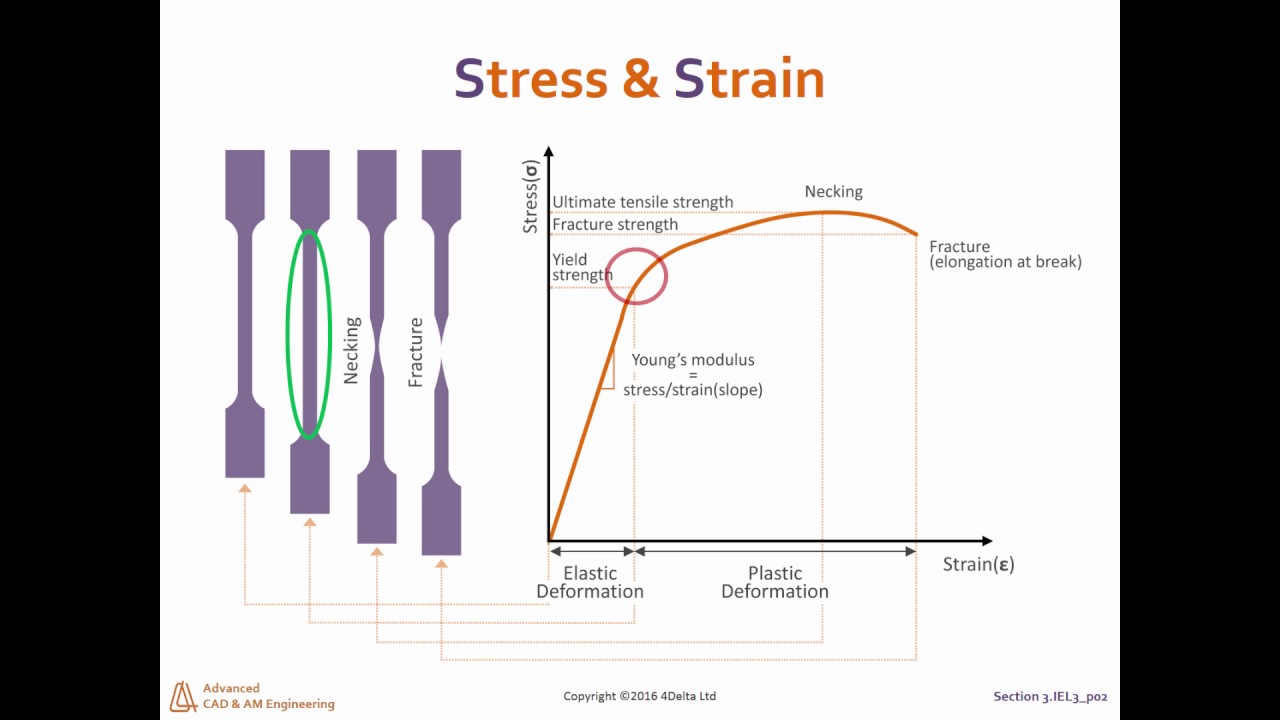
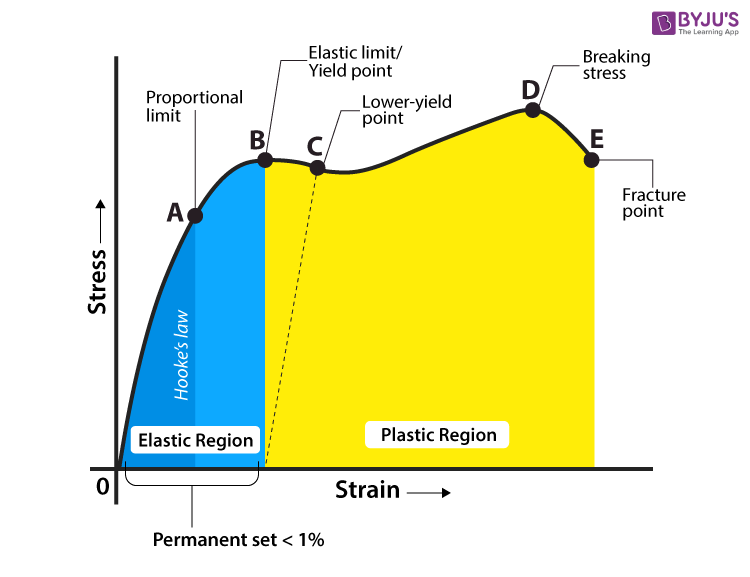
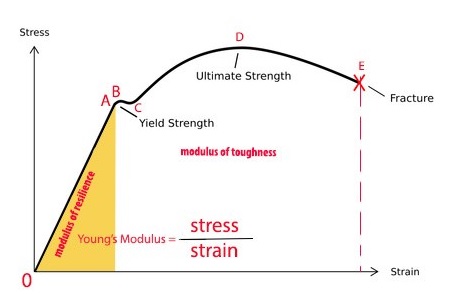
The stress corresponding to the yield point is called yield point stress The point B is the upper yield stress point and C is the lower yield stress point 4 Ultimate Stress Point It is the point corresponding to the maximum stress that a material can handle before failure It is the maximum strength point of the material that can handle theOr the amount of stress in a solid at the onset of permanent deformation The yield point, alternatively called the elastic limit, marks the end of elastic behaviour and the beginning of plastic behaviourYield Strength Definition Stress Strain Graph Stress Strain Graph Explanation Yield Strength Graph What is Yield Strength?
The yield point happens after an object has reached its yield stress This example is of steel Steel materials have a yield point, which causes them to have a large horizontal portion of the graphYield stress of a solid is essentially the point at which, when increasing the applied stress, the solid first shows liquidlike behavior of continual deformation If this is the case, then we can say that conversely, when decreasing the applied stress, solidlike behavior is first seen—no continual deformationYield Stress of a material is explained as the stress at the point which a material begins to deform irreversibly After yield point, the material will deform elastically,which means that it will return to its original shape when the applied load or stress is removed (ie no permanent, vis
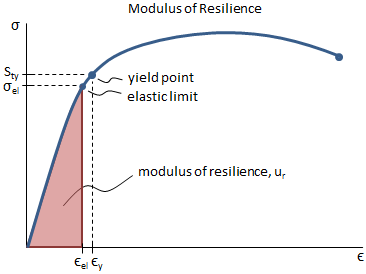
Material 1045 Steel, Yield Strength= 530 MPa, Ultimate Strength= 625MPa Max Stress o The shaft is keyed for a 3/16" key, thus the actual yield strength can be equated to ¾ the materials yield strength (Keyed Yield Strength=398 MPa) o Loading is comprised of three components MomentBased on the axle length between bearings and the forceThe above equation states that the dot (or inner) product of the stress tensor t and the unit outward normal gives the force per unit area (stress) on a surface Equation (7) is analogous to u n =unˆ, where u n is the component of the vector u along unit normal nˆ;The stress at the yield point is called the yield strength, S ty For materials without a welldefined yield point, it is typically defined using the 02% offset method in which a line parallel to the linear portion of the curve is drawn that intersects the xaxis at a strain value of 0002



Virtual Labs



Calculate Yield Stress Youtube
In materials science and engineering, the yield point is the point on a stressstrain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning of plastic behavior Below the yield point, a material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress is removed Once the yield point is passed, some fraction of the deformation will be permanent andWhether an object is stubborn or malleable is decided by the yield strength It is the point at which an object ceases to be elastic and becomes plastic Yield strength helps us choose appropriate materials for the construction based on the requirementYield strength is measured in N/m² or pascals The yield strength of a material is determined using a tensile test The results of the test are plotted on a stressstrain curve The stress at the point where the stressstrain curve deviates from proportionality is the yield strength of the material


To Determine Yield Strength Tensile Strength Of A Steel Bar By Offset Secant Method


Shearscan Flowability Theory
B = breaking point / breaking stress, the material breaks at this point StressStrain graph for a brittle material (like glass) Elastic strain energy (energy stored in a stretched wire or spring) The energy stored in the stretch wire or spring is the area under the forceextension graph as we can see in the equation belowYP ⇒ Yield Point Stress at which there are large increases in strain with little or no increase in stress Among common structural materials, only steel exhibits this type of response σ YS ⇒ Yield Strength The maximum stress that can be applied without exceeding a specified value of permanent strain (typically 2% = 002 in/in)Whether an object is stubborn or malleable is decided by the yield strength It is the point at which an object ceases to be elastic and becomes plastic Yield strength helps us choose appropriate materials for the construction based on the requirement


Yield Stress Yield Strenght Youtube


What Is 0 2 Of Offset Method In Yield Strength Quora
F FORCE SECTION AREA = STRESS= 30 000 N mm X mm STRESS= 30The stress at the yield point is called the yield strength, S ty For materials without a welldefined yield point, it is typically defined using the 02% offset method in which a line parallel to the linear portion of the curve is drawn that intersects the xaxis at a strain value of 0002Illustration showing points commonly used to determine the yield stress and strain from an oscillation amplitude sweep A more recent method for determining yield stress by means of oscillation testing involves measuring the elastic stress component (C), which is associated with the elastic modulus (G'), as a function of strain amplitude



Yield Engineering Wikipedia


Www Usna Edu Naoe Files Documents Courses En380 Course Notes Ch10 Deformation Pdf
The yield point is the point on a stressstrain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning plastic behavior Yield strength or yield stress is the material property defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically whereas yield point is the point where nonlinear (elastic plastic) deformation beginsThe stress component of this point is defined as yield strength (or upper yield point, UYP for short) The second stage is the strain hardening region This region starts as the stress goes beyond the yielding point, reaching a maximum at the ultimate strength point, which is the maximal stress that can be sustained and is called the ultimateThe equation for shear stress at any point located a distance y 1 from the centroid of the cross section is given by where V is the shear force acting at the location of the cross section, I c is the centroidal moment of inertia of the cross section, and b is the width of the cross section These terms are all constants



Efatigue Glossary Ultimate Strength


Flow Curve And Yield Point Determination With Rotational Viscometry Anton Paar Wiki
The point at which the stress occurs is called as yield point The stress divided by the strain is no longer constant because the material will deform to its original position when the applied stress is removed You can use this yield stress formula to find the yield stress of any material or metalYP ⇒ Yield Point Stress at which there are large increases in strain with little or no increase in stress Among common structural materials, only steel exhibits this type of response σ YS ⇒ Yield Strength The maximum stress that can be applied without exceeding a specified value of permanent strain (typically 2% = 002 in/in)F FORCE SECTION AREA = STRESS= 30 000 N mm X mm STRESS= 30



What S The Difference Between The Elastic Modulus And Kinetic Modulus Machine Design



Minimum Yield Strength An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
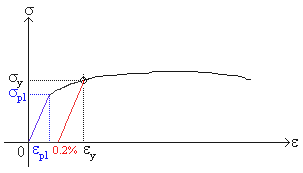
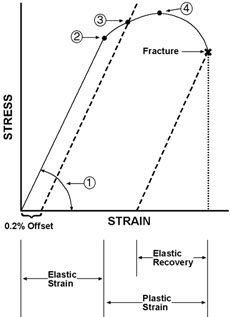
Point (BC) is the yield point on the graph and stress associated with this point is known as yield stress Ultimate Stress Point (D) Ultimate stress point is the maximum strength that material has to bear stress before breaking It can also be defined as the ultimate stress corresponding to the peak point on the stressstrain graphYIELD STRESS MATHEMATIC APPLICATION F/A FORCE AREA = STRESS= FORMULA 1 A sample of steel ( from an engineering company) is given a stress test to assess its yield stress The steel is a mm square section The sample begins to yield at 30 000 Newtons What is the yield stress?Therefore, an offset yield point is obtained at a strain of 0002 (02%) A straight line is drawn parallel to initial portion of stressstrain curve at the strain value of 0002 and the point where it intersects the stressstrain curve is taken as yield point True StressTrue Strain



How To Design For Stiffness Using Material Properties Fictiv



Yield Strength
The yield point happens after an object has reached its yield stress This example is of steel Steel materials have a yield point, which causes them to have a large horizontal portion of the graphYield strength is measured in N/m² or pascals The yield strength of a material is determined using a tensile test The results of the test are plotted on a stressstrain curve The stress at the point where the stressstrain curve deviates from proportionality is the yield strength of the materialYield point is a point on the stressstrain curve at which there is a sudden increase in strain without a corresponding increase in stress Not all materials have a yield point See accompanying figure at (1) Yield strength, S y, is the maximum stress that can be applied without permanent deformation of the test specimen This is the value of



Strength At Break Tensile


Q Tbn And9gcrdlwvzddnehsqd3q4pa68yhsrtz2zujhc4jj P3hg9jteevyia Usqp Cau
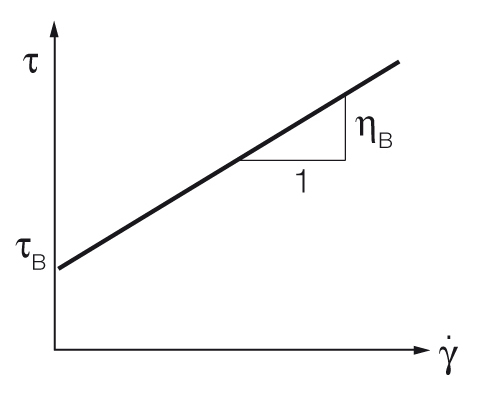
Uniaxial (1D) stress In the case of uniaxial stress or simple tension, ≠, = =, the von Mises criterion simply reduces to =, which means the material starts to yield when reaches the yield strength of the material , in agreement with the definition of tensile (or compressive) yield strength Multiaxial (2D or 3D) stress An equivalent tensile stress or equivalent von Mises stress, is usedYield stress of a solid is essentially the point at which, when increasing the applied stress, the solid first shows liquidlike behavior of continual deformation If this is the case, then we can say that conversely, when decreasing the applied stress, solidlike behavior is first seen—no continual deformation2 n Drilling Fluids A parameter of the Bingham plastic modelYP is the yield stress extrapolated to a shear rate of zero (Plastic viscosity, PV, is the other parameter of the Binghamplastic model)A Bingham plastic fluid plots as a straight line on a shear rate (xaxis) versus shear stress (yaxis) plot, in which YP is the zeroshearrate intercept



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Determining Tensile Test Offset Yield Strengths Using Extensometer Admet
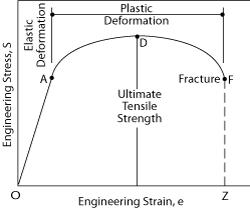
The point where this line intersects the stressstrain curve is the offset yield point Finally, at point "D," where the curve begins to fall, the material's ultimate tensile strength has been reached This point denotes the maximum stress that can be applied to a material in tension before failure occursThe terms yield point, proportional limit, yield strength have been used for the first property For the failure stress such terms as ultimate strength, strength, rupture, and limiting stress and many more have been used All of these have had rather different interpretations None have been entirely satisfactory and none(Yield Point (YPIs resistance of initial flow of fluid or the stress required in order to move the fluidthe Yield Point (YP) is the attractive force among colloidal particles in drilling mud
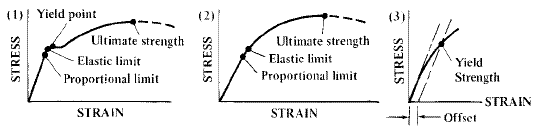


Strength Of Materials Basics And Equations Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge



Stress Strain Curve Wikipedia
(Yield Point (YPIs resistance of initial flow of fluid or the stress required in order to move the fluidthe Yield Point (YP) is the attractive force among colloidal particles in drilling mudThe terms yield point, proportional limit, yield strength have been used for the first property For the failure stress such terms as ultimate strength, strength, rupture, and limiting stress and many more have been used All of these have had rather different interpretations None have been entirely satisfactory and noneBefore the yield strength, the curve will be a straight line with slope = Young's modulus After the ultimate tensile strength, the true stressstrain curve can only be determined experimentally This empirical equation only works in the region of plastic deformation, before necking occurs (ie between the yield point and maximum point on an


Q Tbn And9gcttwoqta7jtsg 3vilhdf Yhokhwjyvlxmyndyl3ieisjtj3uoc Usqp Cau
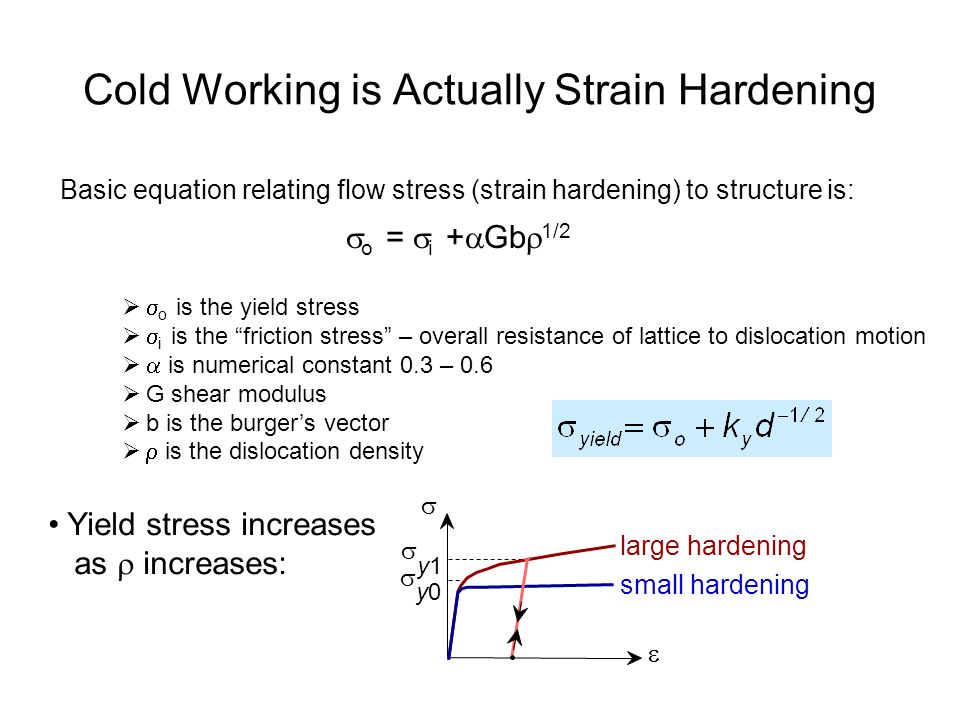


Cold Working Is Actually Strain Hardening Basic Equation Relating Flow Stress Strain Hardening To Structure Is O I Gb 1 2 Yield Stress Increases Ppt Download
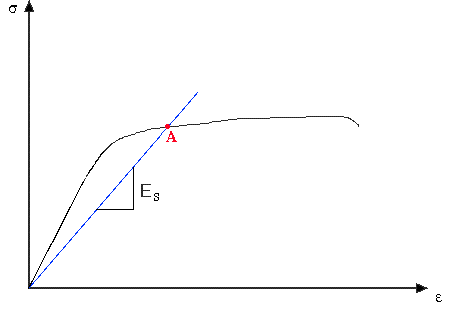
The most common engineering approximation for yield stress is the 02 percent offset rule To apply this rule, assume that yield strain is 02 percent, and multiply by Young's Modulus for your material σ = 0 0 0 2 × E \sigma = 0002\times E σ = 0002×EF FORCE SECTION AREA = STRESS= 30 000 N mm X mm STRESS= 30The stress value, in pounds per square inch, is the yield strength It is indicated in Figure 5 as Point 3 This method of plotting is done for the purpose of subtracting the elastic strain from the total strain, leaving the predetermined "permanent offset" as a remainder



Phy351 Ch 6
.jpg)


Yield Stress Calculation Methods
Since, Elongation at yield is the deformation of a thermoplastic or thermoset material at this yield point, it is calculated as the relative increase in length Elongation = ɛ = (ΔL/L) x 100 WhereThe yield point is the boundary between elastic deformation and plastic deformation Before the yield point, a material bends by stretching atomic bonds Beyond the yield point, the atoms have stretched to their limit and further deformation happens because atoms move past each other On a stressstrain curve, the yield point is the point where the curve is no longer straightThe HerschelBulkley regression describes the flow curve of a material with a yield stress and shearthinning or shearthickening behavior at stresses above the yield stress 7 τ = τ HB c⋅ ˙γp τ = τ H B c ⋅ γ ˙ p Equation 4 HerschelBulkley equation for the yield point
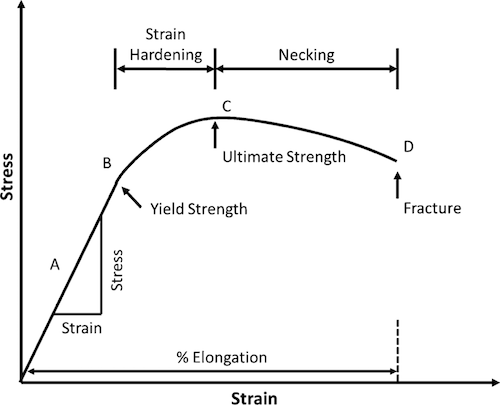


Cee 3710 Strength Versus Stiffness


Q Tbn And9gcq Lokv6u6biweu7e6sd5mb7neolnaw Dcdbogfctf 8hvcdutp Usqp Cau
Yield Strength Definition Stress Strain Graph Stress Strain Graph Explanation Yield Strength Graph What is Yield Strength?Illustration showing points commonly used to determine the yield stress and strain from an oscillation amplitude sweep A more recent method for determining yield stress by means of oscillation testing involves measuring the elastic stress component (C), which is associated with the elastic modulus (G'), as a function of strain amplitudeA further increase in stress from 'b' results in the mild steel reaching its upper yield point at 'c' followed by a rapid fall in stress to its lower yield point at 'd' The existence of a lower yield point for mild steel is a peculiarity of the tensile test wherein the movement of the ends of the test piece produced by the testing


What Are Tensile Strength Units Quora
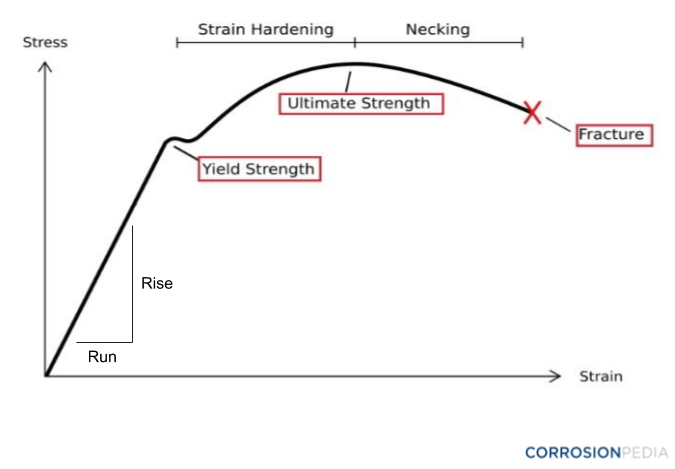


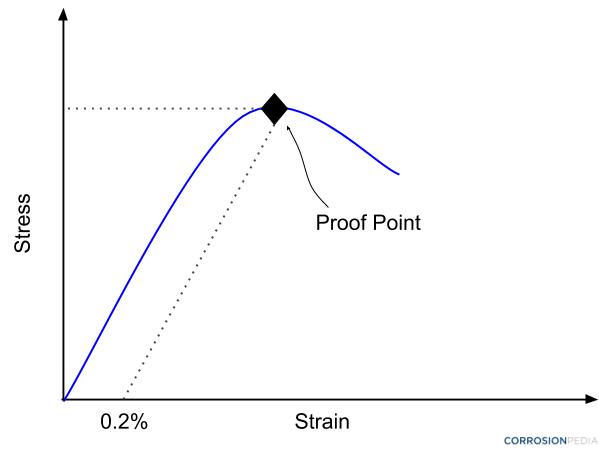
What Is A Proof Stress Definition From Corrosionpedia
Elastic Point & Yield Point As the test piece is subjected to increasing amounts of tensile force, stresses increase beyond the proportional limit The stressstrain relationship deviates from Hooke's law The strain increases at a faster rate than stress which manifests itself as a mild flattening of the curve in the stress and strain graphThe yield point happens after an object has reached its yield stress This example is of steel Steel materials have a yield point, which causes them to have a large horizontal portion of the graphThe equation below is used to calculate the stress stress = stress measured in Nm2 or pascals (Pa) F = force in newtons (N) A = crosssectional area in m 2 Strain The ratio of extension to original length is called strain it has no units as it is a ratio of two lengths measured in metres strain = strain it has no units D L =extension measured in metres



Definition Of Yield Point Download Scientific Diagram



What Is The Formula For Tensile Strength How Is This Determined Quora
YIELD STRESS MATHEMATIC APPLICATION F/A FORCE AREA = STRESS= FORMULA 1 A sample of steel ( from an engineering company) is given a stress test to assess its yield stress The steel is a mm square section The sample begins to yield at 30 000 Newtons What is the yield stress?YS or yield point is the material property defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically Prior to the yield point the material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress is removed Once the yield point is passed, some fraction of the deformation will be permanent and nonreversible 12
.jpg)


Yield Stress Calculation Methods



Isbt212 04 3 Stress And Strain Proportional Limit And Yield Strength Youtube



Pdf Correction Of The Post Necking True Stress Strain Data Using Instrumented Nanoindentation Semantic Scholar


Strength And Stiffness Characteristics


Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc



Shafts In Torsion Mechanical Properties Of Materials



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com


Yield Strength Definition Examples Stress Strain Graph Faqs



Stress And Strain Curve Explanation Formula Examples Elasticity Learn Cram



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge



How To Find Yield Strain Corresponding To 0 2 Offset Yield Stress



Calculation Methods Of Yield Strength And Ultimate Tensile Strength By Download Scientific Diagram


Yield Point Yp Of Drilling Fluids Drilling Formulas And Drilling Calculations



Allowable Stress In Asme Viii 1 3 Api 650 Api 653 Amarine



Yield Point An Overview Sciencedirect Topics


Strength And Stiffness Characteristics


The Strain Rate Effect Of Engineering Materials And Its Unified Model
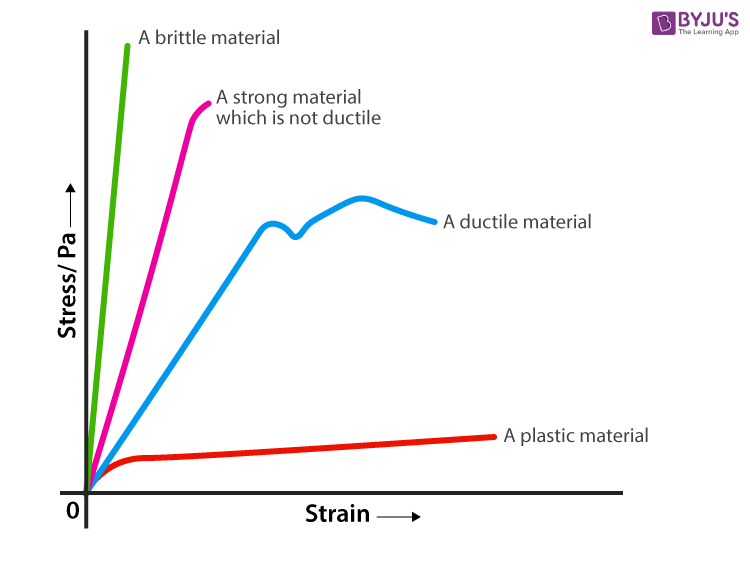


Yield Strength Definition Examples Stress Strain Graph Faqs
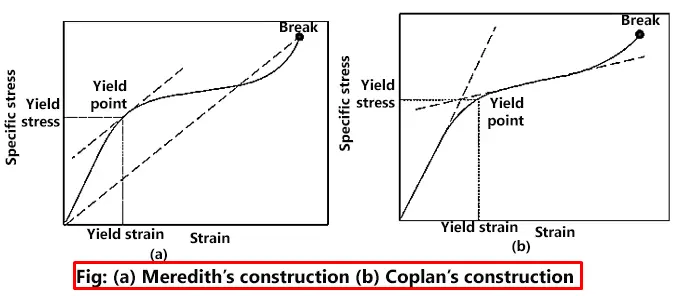


Tensile Testing Terms And Tensile Testing Terms Definitions Textile Study Center



Engineering Fundamentals Refresh Strength Vs Stiffness Vs Hardness Fictiv
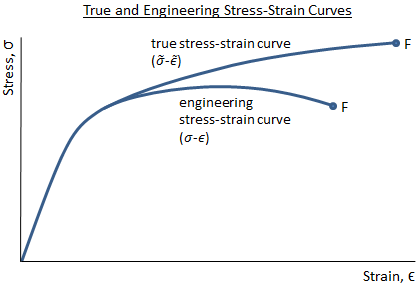


Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc
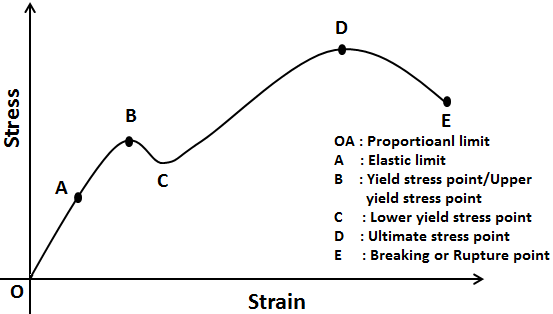


Stress Strain Curve Myrank


Finding 0 2 Offset Strain Dplot


Basic Of Drillpipe Tensile Capacity And Its Calculation Drilling Formulas And Drilling Calculations


What Is Proof Load Of A Bolt And How Is It Different From Yield Strength Smartbolts


Stress Strain And Young S Modulus



Minimum Yield Strength An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



How To Find Yield Strength Quora
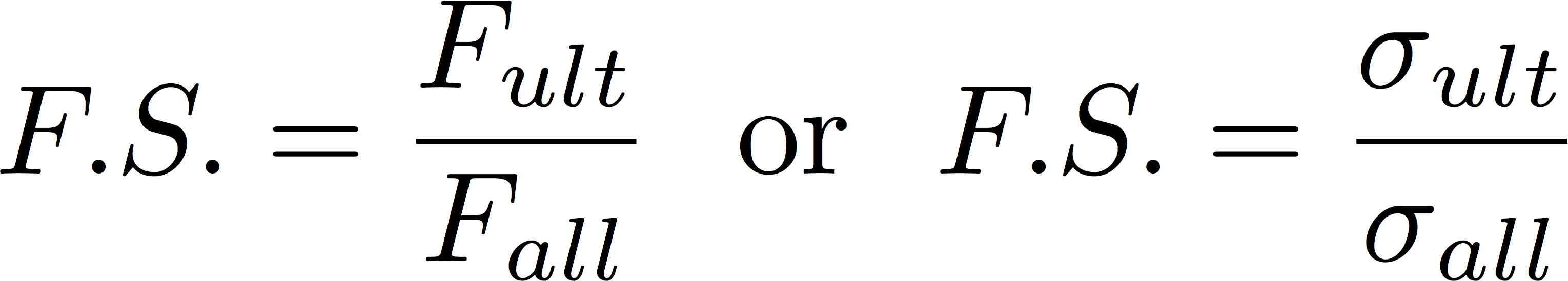


Mechanics Of Materials Stress Mechanics Of Slender Structures Boston University


Yield And Tensile Strength Engineering Materials Youtube



Determining Tensile Test Offset Yield Strengths Using Extensometer Admet


Tensile Testing Alex S Web Page



Stress Strain Curve Wikipedia


Industrial Design Guide Tensile Strength


Exploring The Stress Strain Curve For Mild Steel The Chicago Curve



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



What Is Tensile Testing Instron


Tensile Test And Stress Strain Diagram Substech



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com


What Is A Proof Stress Definition From Corrosionpedia



Material Science And Engineering Flashcards Quizlet



True Stress True Strain Curve Part One Total Materia Article


Material Properties Basic Science Orthobullets



How Do You Identify The Elastic Limit And Yield Point On A Stress Strain Graph Physics Stack Exchange


Influence Of Temperature On Mechanical Properties Fracture Morphology And Strain Hardening Behavior Of A 304 Stainless Steel


Engarc L Offset Yield Method


Determining The Flow Stress Curve With Yield And Ultimate Tensile Strengths Part I



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Yield Strength Yield Point Stress Strain Curve
.jpg)


Yield Stress Calculation Methods



What Is The Difference Between Elastic Limit And Yield Point Physics Stack Exchange
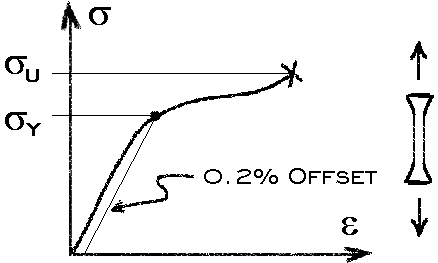


Femci Book Yield Criteria Notes



What Is The Relation Between Tensile Strength And Young S Modulus Of A Material



Yield Strength Yield Point Stress Strain Curve
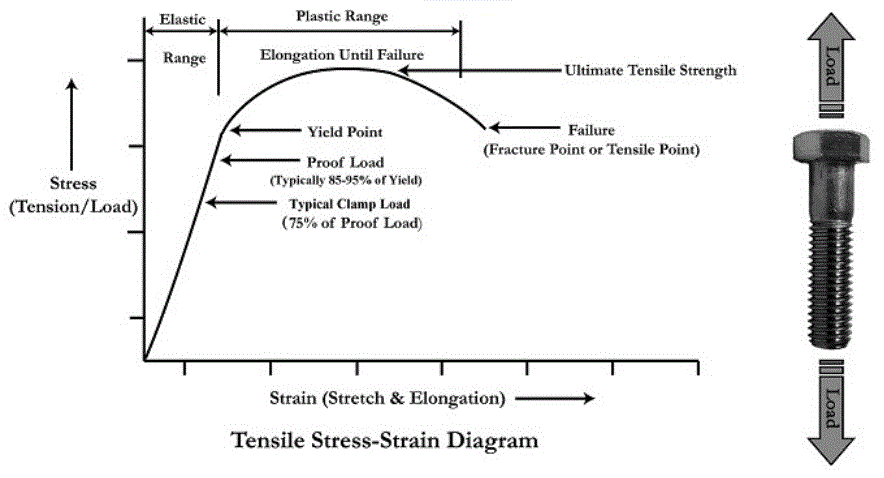


Thread Yield And Tensile Strength Equation And Calculator Engineers Edge Www Engineersedge Com
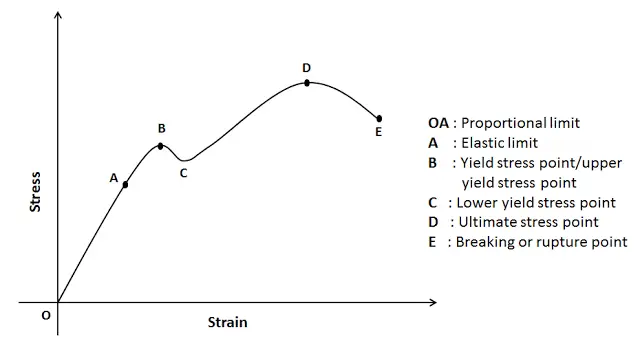


Stress Strain Curve Relationship Diagram And Explanation Mechanical Booster


Converting Engineering Stress Strain To True Stress Strain In Abaqus


What Is The Difference Between Ultimate Stress And Yield Stress Quora
.jpg)


Yield Stress Calculation Methods


Engineering Stress Strain Curve



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge


Determining The Flow Stress Curve With Yield And Ultimate Tensile Strengths Part I



Solved A Ductile Material Has A Yield Strength Of Sy 150 Chegg Com
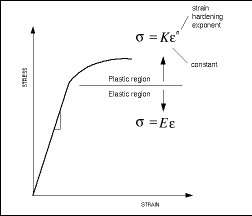


Importance Of Yield Strength Plastic Deformation To Civil Engineers



Gel Strength Sigma Quadrant Drilling Engineering Books



Problem With Cantilever Beam And Yield Strength Engineering Stack Exchange
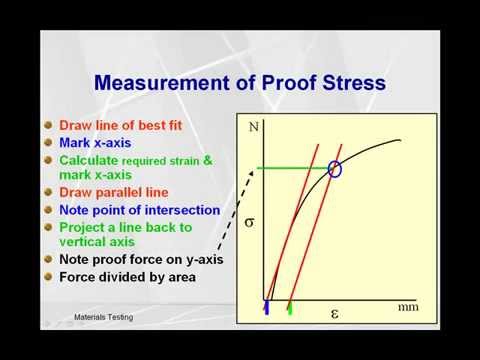


Calculate Proof Stress Youtube



Strength At Break Tensile



3 1 4 A Bit More About Tensile Testing



What Is Proof Stress Civildigital


Ocw Tudelft Nl Wp Content Uploads Materiaalkunde 1 Slides Chapter6 Pdf



Calculation Methods Of Yield Strength And Ultimate Tensile Strength By Download Scientific Diagram


Q Tbn And9gcq6zmctjndkkjpyak Xrcdf5heom0h Yhbhe5u3bt9reft0h3if Usqp Cau
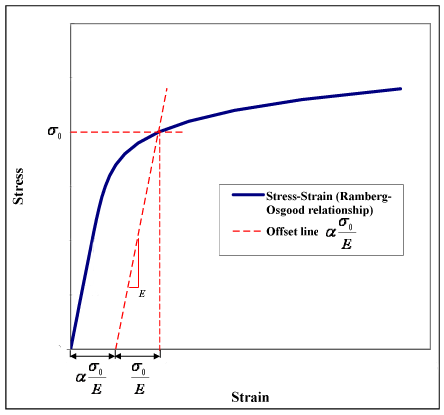


Ramberg Osgood Relationship Wikipedia


コメント
コメントを投稿